What is a domain?
A domain is a unique address that identifies a website on the Internet. It allows users to find and access a specific website. Before the existence of domains, it was necessary to access a website by directly entering its IP address. With the appearance of domains, the situation changed and instead of using the IP address, we use the chosen domain.
Domains are made up of a name and an extension like .com, .org, or .net.
Components of a Domain:

- Domain Name: The personalized and specific part, such as "thedomainiwant" in "thedomainiwant.com". It is one of the most important parts, by which users will know you, so it is important to be clear about the desired name or what you want to convey/achieve with that name.
- Domain Extension (TLD): Also known as TLD (Top-Level Domain), it is the part that follows the name, like .com, .net, .org, .es, .cat, etc.
There are several types of domain extensions (gTLD, ngTLD, ccTLD, and third level), although the operation of the services associated with the domain will not vary from the chosen TLD, the requirements and proper functioning of the domain may vary. For example, it is common for territorial extensions (ccTLD) to require that the contact person has a presence in the relevant country.
Subdomain
Creating subdomains will allow you to organize different sections of a website or create sites related to the main domain. For example:
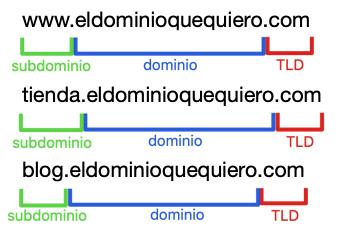
- www.thedomainiwant.com: Main webpage (Web application like WordPress)
- store.thedomainiwant.com: Online business store (Web application like PrestaShop)
- blog.thedomainiwant.com: Web with help guides.
Domain Functions:
- Website: Host an information page of our business, an online store, a management system, etc.
- Email: Create personalized email accounts from our own domain (Example: info@thedomainiwant.com)
- Easy Access: Allows users to access a website through an easy-to-remember address, instead of using a numeric IP address.
- Identity and Brand: Helps define the identity of a website and email accounts and is crucial for the brand and online presence of a business or organization.
- Web Traffic Management: Domains can point to specific servers via DNS records, managing how and where user requests are directed.
In summary, a domain is a unique and readable address that allows access to a website on the Internet, facilitating navigation and identification.
What Entities Are Involved in the Process?
- ICANN: is the organization responsible for assigning Internet protocol address space, protocol identifiers, and domain name management functions, as well as administering the root server system. In short, the organization that manages the functioning of the Internet.
- Registries: the Registry is the entity that manages one or more specific extensions, for example, Verisign manages the extensions .com, .de, .tv, .ai.
- Registrars: the registrar is the company that manages the registration of the domain and maintains it for the duration of that registration, for example, us.
- Resellers: the reseller is a third person or company that resells a third party's service.
- Registrants: the registrant is the domain holder, that is, the final person or company making the registration.